Cloud Computing – A Primer For Small Business Owners
Cloud Computing – A Primer For Small Business Owners
Sairam J, Director, Global Clouds Consultants, Dec 28, 2021

As a Cloud Consultant, while talking to various small and mid-sized business (SMB) owners, I am often asked these questions – what is cloud computing, what’s in for me, how do I get started? Most importantly, in these challenging times, how does Cloud help to differentiate my business.
Let’s begin with the basics!
What is Cloud Computing?
According to National Institute of Standards & Technology (NIST), cloud computing is defined as “a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources, that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.”
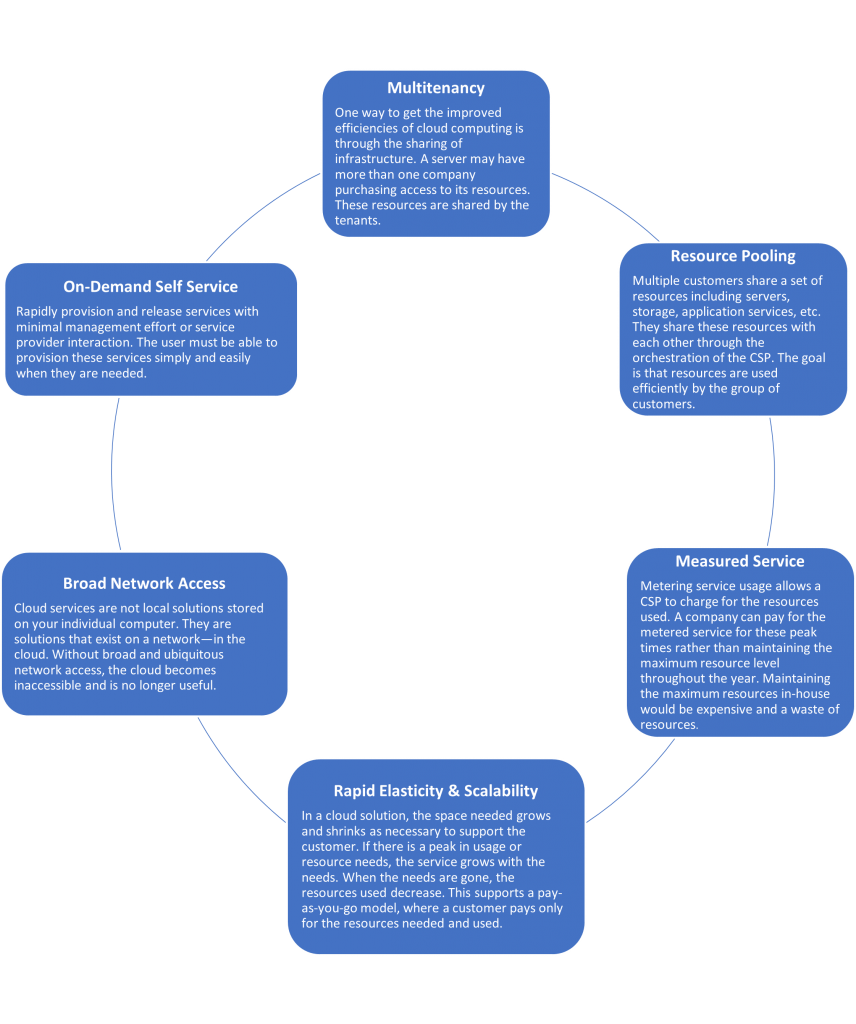
Key Cloud Characteristics
Understanding the key characteristics of cloud computing will allow you to distinguish between cloud solutions and non-cloud solutions.
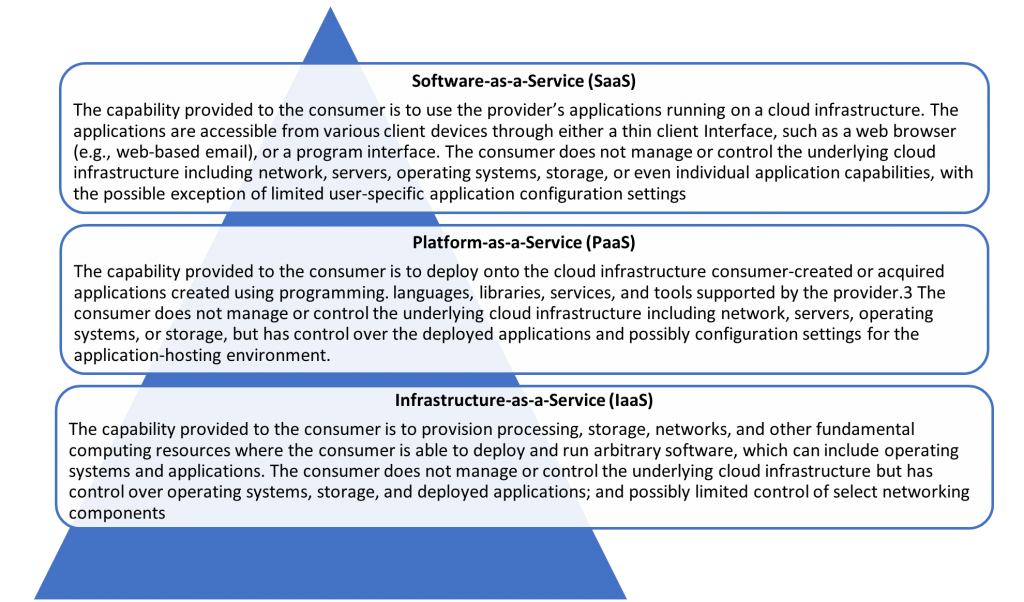
Cloud Service Categories
Cloud Deployment Models
● Private Cloud : A private cloud belongs to a single company and contains data and services for use by that company.
● Public Cloud : The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for open use by the general public. It may be owned, managed, and operated by a business, academic, or government organization, or some combination of them. It exists on the premises of the cloud provider.
● Community Cloud : The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a specific community of consumers from organizations that have shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations).
● Hybrid Cloud : A hybrid cloud can be a combination of any of the other cloud deployment models but is usually a combination of the private and public cloud deployment models.
Cloud Considerations
● Interoperability : Interoperability creates the ability to communicate with and share data across multiple platforms and between traditional and cloud services provided by different vendors. Avoiding vendor lock-in allows the customer to make decisions based on the cost, feature set, or availability of a particular service regardless of the vendor providing the service. Interoperability leads to a richer set of alternatives and more choices in pricing.
● Portability : Portability may refer to data portability or architecture portability. Data portability is focused on the ability to move data between traditional and cloud services or between different cloud services without having to port the data under challenging and lossy methods or significant changes to either service or the loss of metadata. Architecture portability is concerned with the ability to access and run a cloud service from a wide variety of devices, running different operating systems.
● Reversibility : Reversibility is a measure of the extent your cloud services can be moved from one cloud environment to another. This includes moving between a cloud environment and an on-premise traditional environment. The movement between environments must be simple and automatic.
● Security : Cloud security is a challenging endeavor. There are aspects of cloud computing, such as multitenancy, that create new complexities to security. The owner of data remains ultimately responsible for the security of the data, regardless of what cloud or non-cloud services are used. Cloud security involves more than protection of the data but includes the applications and infrastructure.
● Privacy : Privacy concerns include access to data both during a contract and at the end of a contract as well as the erasure or destruction of data when requested or as required within the contract. Regulatory and contractual requirements such as HIPAA and PCI are also key concerns.
● Resiliency : Resilience is the ability to continue operating under adverse or unexpected conditions. This involves both business continuity and disaster recovery planning and implementation. Business continuity might dictate that a customer stores their data in multiple regions so that a service interruption in one region does not prevent continued operations. The cloud also provides resiliency when a customer suffers a severe incident such as weather, facilities damage, terrorism, civil unrest, or similar events. A cloud strategy allows the company to continue to operate during and after these incidents.
● Performance : Performance is measured through a Service Level Agreement (SLA). Performance of a cloud service is generally quite high as major Cloud Service Providers build redundancy into their systems. The major performance concerns are network availability and bandwidth.
● Governance : Cloud governance uses the same mechanisms as governance of your on-premises IT solutions. This includes policies, procedures, and controls. Controls include encryption, access control lists (ACLs), and identity and access management.
● Maintenance & Versioning : Maintenance & versioning in a cloud environment is a joint responsibility of a Cloud Consumer and a Cloud Service Provider. Each party is responsible for the maintenance and versioning of their portion of the cloud stack.
● Service Levels & Service Level Agreements : Contractually, an SLA specifies the required performance parameters of a solution. This negotiation will impact the price, as more stringent requirements can be more expensive.
● Resiliency : Resilience is the ability to continue operating under adverse or unexpected conditions. This involves both business continuity and disaster recovery planning and implementation. Business continuity might dictate that a customer stores their data in multiple regions so that a service interruption in one region does not prevent continued operations. The cloud also provides resiliency when a customer suffers a severe incident such as weather, facilities damage, terrorism, civil unrest, or similar events. A cloud strategy allows the company to continue to operate during and after these incidents.
● Auditability : A cloud solution needs to be auditable. This is an independent examination of the cloud services controls, with the expression of an opinion on their function with respect to their purpose. Are the controls properly implemented? Are the controls functioning and achieving their goal? These are the questions of an auditor.
● Regulatory : A regulatory environment is one where a principle or rule controls or manages an organization. One form of regulations are those governmental requirements that have the force of law. Another form of regulations is those put in place through contractual requirements. A third form of regulations is found through standards bodies like International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and NIST as well as nongovernmental groups such as the Cloud Security Alliance and the Center for Internet Security.
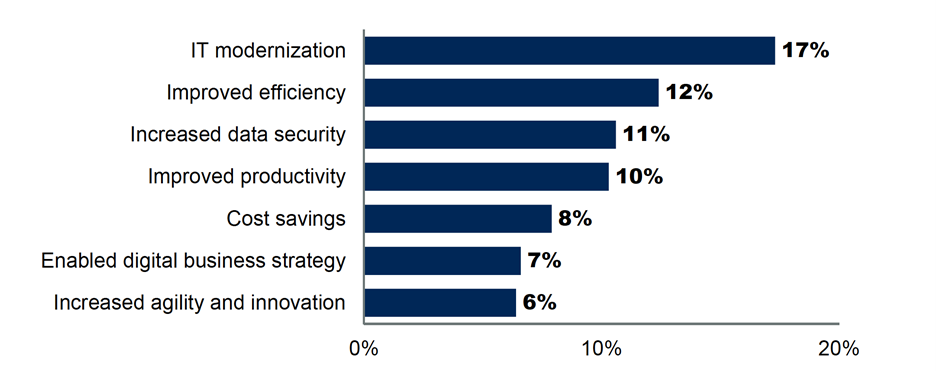
Cloud Benefits

As per the Gartner Research, top outcomes achieved by Cloud are as below:
Conclusion
As per the Gartner Research, by 2025, cloud computing will be pervasive. Cloud will drive not only technological innovation, but also serve as the foundation for business innovation. In order for any businesses to thrive, including Small & Mid-sized businesses, it is very important for the business strategies to include Cloud Strategies.
In today’s challenging times, it is imperative for businesses to create newer business models and use Cloud Computing as business disruptor!
The future of Cloud is, Cloud will be everywhere in next few years! Are you there yet?
Next Step
Some of the top challenges to adopt Cloud computing are:
– Insufficient Skills
– Security Concerns
– Higher Costs
– Business Value
– Culture change
In order to get started, Start Small, Grow Big! Eliminate the risk factors, focus on creating newer business models that will help to differentiate your business!